Menu
Close
Picture this: You're running a successful business, everything is running smoothly, and then disaster strikes. Your systems crash, your data is lost, and chaos ensues. It's every entrepreneur's worst nightmare. But fear not! There is a solution – disaster recovery.
Disaster recovery is the process of planning and implementing strategies to ensure that your business can recover from any unforeseen events or emergencies. Whether it's a natural disaster, cyber-attack, or hardware failure, having a solid disaster recovery plan in place can mean the difference between getting back on track quickly or facing catastrophic consequences.
In this article, we will delve into the world of disaster recovery – its definitions, importance, key goals - as well as explore different types of outages and pain points associated with it.

Disaster recovery planning is not just a nice-to-have, it's an essential aspect of any business's overall strategy. The importance of disaster recovery planning cannot be overstated, it refers to the process of restoring operations and data after an unexpected event or outage, such as a natural disaster, cyber-attack, or hardware failure. The primary goal of disaster recovery is to minimise downtime and ensure that critical systems and information are quickly restored.
One key reason why disaster recovery planning is crucial is that it helps minimise downtime and loss of productivity. When a disaster strikes, whether it's a natural calamity or a cyber-attack, businesses need to have measures in place to ensure they can quickly restore their systems and resume operations. Without proper planning, organisations risk extended periods of downtime which can result in significant financial losses and damage to their reputation.
In today's digital age, where businesses rely heavily on technology for their day-to-day operations, the importance of disaster recovery planning cannot be overstated. Without proper preparation, organisations risk not only financial loss but also damage to their reputation and customer trust.
One key aspect of disaster recovery is identifying the different types of outages that can occur. Unplanned outages refer to sudden disruptions in service due to unforeseen events like power failures or network issues. On the other hand, planned outages are intentional interruptions caused by system upgrades or maintenance.
Businesses often face several pain points when it comes to implementing effective disaster recovery strategies. These include limited resources and budget constraints, lack of expertise in managing complex IT infrastructure, and difficulty in prioritising which systems should be recovered first.
It's essential to understand that disaster recovery is not synonymous with high availability (HA). While HA focuses on preventing downtime through redundant systems and failover mechanisms within one location or data centre, disaster recovery involves having DR sites in separate geographic locations.
Cloud deployment has become increasingly popular for disaster recovery purposes due to its scalability and cost-efficiency. By leveraging cloud-based solutions for backup storage and virtual machine replication, businesses can ensure they have off-site copies readily available without investing in additional physical infrastructure.
Another important aspect of disaster recovery planning is data protection. Businesses today rely heavily on digital information - customer records, financial data, proprietary software - all these are critical assets that need to be safeguarded. Disaster recovery plans include strategies for regular backups and offsite storage so that even if primary systems fail or are compromised, there are copies available for restoration.
In addition to minimising downtime and protecting data assets, disaster recovery planning also helps with compliance requirements. Many industries have specific regulations regarding data security and privacy (such as HIPAA for healthcare) that organisations must adhere to. Having robust disaster recovery procedures in place ensures compliance with these regulations by demonstrating proactive measures taken towards securing sensitive information.
Furthermore, having a comprehensive disaster recovery plan also enhances internal confidence among employees and stakeholders alike. Knowing that the organisation has thought through potential risks and has contingencies in place provides reassurance during times of crisis or uncertainty.
The importance of disaster recovery planning lies in its ability to mitigate risks proactively rather than reactively dealing with them after they occur. It enables businesses to maintain continuity amid unforeseen circumstances while safeguarding critical resources such as data integrity and employee morale.
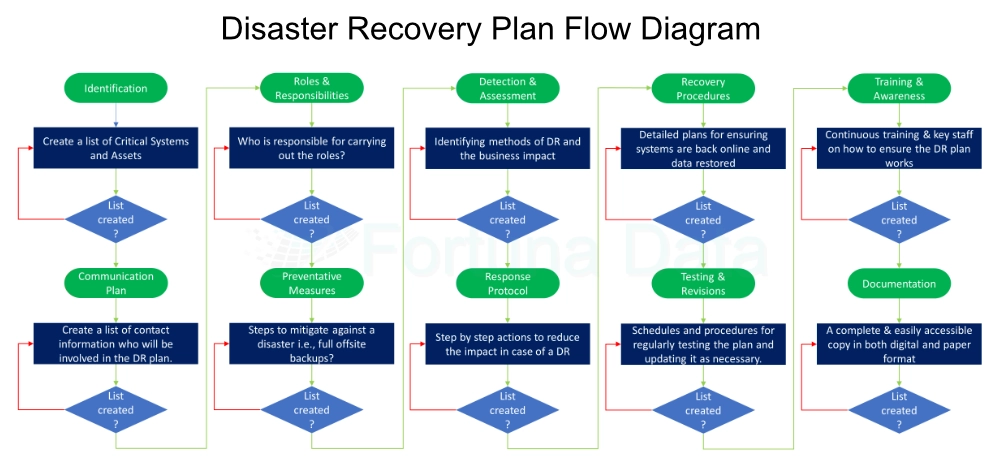
Below are key points a business needs to understand in order to successfully recover from a disaster.
Think of this as a comprehensive "picture" or roadmap that an business would follow in the event of a disaster to ensure quick recovery and minimal impact.
When it comes to disaster recovery, there are several key goals that organisations aim to achieve. First and foremost, the primary goal is to minimise downtime and ensure business continuity. This means having a plan in place to quickly recover systems and data in the event of a disaster or outage.
Another important goal is to maintain data integrity. Disaster recovery strategies should focus on preserving the accuracy and consistency of critical data during the recovery process. This involves implementing robust backup solutions, conducting regular tests, and ensuring that data synchronisation points are properly defined.
Additionally, disaster recovery aims to mitigate financial losses caused by disruptions. By having a solid plan in place, businesses can reduce the impact of downtime on their revenue streams and customer satisfaction levels.
Furthermore, disaster recovery efforts strive to protect an organisation's reputation. In today's digital age where news spreads rapidly through social media platforms, any extended period of system unavailability can result in negative publicity for companies.
Lastly but certainly not least, disaster recovery plays a crucial role in complying with industry regulations and meeting legal requirements regarding data protection. Organisations must ensure that they have adequate safeguards in place to secure sensitive information and adhere to any applicable privacy laws.
These key goals highlight why implementing effective disaster recovery strategies is essential for businesses of all sizes. It's not just about recovering from unexpected events; it's about safeguarding your operations, maintaining customer trust, and ensuring long-term success. So don't wait until it's too late – start planning your disaster recovery strategy today!
Outages can disrupt business operations and cause significant financial losses. Understanding the different types of outages is crucial for developing an effective disaster recovery plan.
Unplanned outages are sudden and unexpected disruptions that occur due to hardware failures, software glitches, or natural disasters. These outages can lead to data loss, system downtime, and a halt in business operations. They require immediate action to restore systems and minimise the impact on the organisation.
Unplanned outages are the stuff nightmares are made of for businesses. These unexpected disruptions to normal operations can occur due to a variety of reasons, such as power failures, natural disasters, hardware or software malfunctions, or even human error. Regardless of the cause, the impact can be devastating.
When an unplanned outage strikes, it can result in significant downtime and loss of productivity. This means that employees may not be able to access critical systems or data needed to perform their tasks efficiently. It also means that customers may experience delays in receiving products or services, leading to frustration and potential damage to a company's reputation.
Unplanned outages can also have financial implications for businesses. The cost of downtime can quickly add up, with estimates ranging from thousands to millions of dollars per hour depending on the sise and nature of the organisation.
To minimise the impact of unplanned outages, disaster recovery strategies should be in place. These strategies involve measures such as data backups and redundancy solutions that allow for quick restoration after an outage occurs.
Dealing with unplanned outages requires proactive planning and preparation. By implementing robust disaster recovery measures, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure continuity even when faced with unexpected disruptions.
Planned outages, on the other hand, are intentionally scheduled by organisations to perform maintenance tasks, upgrades, or other activities that require system downtime. Unlike unplanned outages, which can cause chaos and disrupt business operations, planned outages allow businesses to minimise the impact on their day-to-day activities.
Although they are planned, they still pose risks if not properly managed. During these outages, businesses must ensure that critical services remain accessible through redundant systems or alternative solutions.
During a planned outage, IT teams can address any potential issues before they become major problems. This proactive approach helps maintain system stability and ensures that critical systems are running smoothly. By taking the time to plan these outages in advance, organisations can avoid unexpected disruptions and reduce the risk of data loss or corruption.
One common type of planned outage is a software upgrade. These upgrades may include new features, bug fixes, or security patches that help keep systems up-to-date and protected against potential threats. By scheduling these upgrades during non-peak hours or low-demand periods, businesses can minimise disruption for end-users while ensuring their systems remain secure.
Additionally, organisations often use planned outages as an opportunity to test disaster recovery plans and procedures thoroughly. Running simulated failover scenarios during scheduled downtime helps ensure that backup systems are functioning correctly and ready for action if an actual disaster occurs.
Both unplanned and planned outages highlight the importance of having a robust disaster recovery strategy in place. By investing in preventive measures such as regular backups, fault-tolerant systems, and redundant infrastructure components, organisations can mitigate potential outage risks.
Understanding the types of outages is essential for developing an effective disaster recovery plan that addresses both unplanned and planned events. Businesses should prioritise preventive measures to minimise downtime and data loss during these disruptive incidents. By investing in proper disaster recovery strategies and operations, organisations can strengthen their resilience against potential outage risks.
Disaster recovery is a critical aspect of any organisation's IT strategy, but it also comes with its fair share of challenges. Let's take a closer look at some of the pain points that organisations may encounter when implementing disaster recovery measures.
One common pain point is the complexity involved in setting up and managing disaster recovery systems. It requires detailed planning, coordination, and ongoing maintenance to ensure that all critical data and applications are properly protected and can be quickly restored in the event of a disaster.
Another challenge is the cost associated with implementing and maintaining robust disaster recovery solutions. From investing in specialised hardware and software to hiring skilled professionals, there are significant financial implications for organisations looking to achieve a high level of resiliency.
Additionally, ensuring data consistency across multiple sites can be quite challenging. Inconsistencies between primary and backup systems can lead to data corruption or loss during failover or switchover processes.
Furthermore, testing the effectiveness of disaster recovery plans can be time-consuming and disruptive to regular business operations. Organisations need to regularly conduct drills and simulations to validate their procedures while minimising potential disruptions.
Keeping up with evolving technologies can pose difficulties for organisations striving for effective disaster recovery strategies. As new threats emerge or technology advancements occur, it becomes necessary to reassess existing plans and adopt new solutions accordingly.
When it comes to protecting your business from potential disruptions, two key terms often come up: disaster recovery and high availability. While they may sound similar, these concepts have distinct differences that are important to understand.
High availability refers to a system or infrastructure that is designed to minimise downtime and ensure uninterrupted access to critical applications or services. It focuses on maintaining continuous operations by implementing redundant components and failover mechanisms.
On the other hand, disaster recovery goes beyond just minimising downtime; it involves comprehensive planning and preparation for worst-case scenarios. Disaster recovery aims to restore systems and data after a major disruption or catastrophic event, such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or hardware failures.
The primary distinction between the two lies in their objectives. High availability prioritises uptime and immediate failover capabilities within an active environment, while disaster recovery centres on recovering operations in a separate environment following a disruptive incident.
While both approaches are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring business continuity, they serve different purposes. A high availability solution can address minor disruptions quickly but may not be sufficient when facing large-scale disasters that require significant restoration efforts.
In contrast, disaster recovery provides organisations with a comprehensive plan of action for recovering critical systems and data in the aftermath of significant incidents. It considers various factors like backup strategies, data replication methods, off-site storage options, and testing procedures.
It's worth noting that high availability solutions can be integrated into an overall disaster recovery strategy to provide additional layers of protection against outages. By combining both approaches effectively based on specific needs and risks faced by your organisation is crucial for achieving optimal resilience during unforeseen events.
By understanding the distinctions between these concepts, you can develop a comprehensive strategy that covers both high availability and disaster recovery, ensuring your business is fully protected.
Disaster recovery strategies and operations are crucial components of any comprehensive disaster recovery plan. These strategies ensure that businesses can quickly recover and resume their operations in the event of a natural or man-made disaster.
One key aspect of disaster recovery is determining the appropriate approach for switching over to a backup system or failing over to another location. Switchover refers to the planned transition from primary systems to backup systems, while failover occurs when an unexpected outage forces a switch to secondary systems.
Cloud deployment has revolutionised disaster recovery by offering scalable and cost-effective solutions. With cloud-based DR, businesses can replicate their critical data and applications in off-site locations, ensuring redundancy and accessibility even during disruptions.
Effective data management is also vital for successful disaster recovery. For databases, maintaining data consistency across multiple sites is essential for seamless failover or switchover processes. This requires careful consideration of synchronisation methods specific to each database technology, such as MySQL or Oracle.
System design plays a pivotal role in effective disaster recovery planning. DR sites should be strategically located away from potential risks like flood-prone areas or earthquake zones. Additionally, defining Recovery Time Objective (RTO) - how quickly operations must be restored -and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) - acceptable amount of data loss - helps determine appropriate backup schedules and resources allocation.
Implementing robust strategies and fine-tuned operational procedures ensures that businesses are well-prepared for unforeseen events that could disrupt normal operations. By leveraging the power of cloud deployments, mastering data management techniques, and designing resilient system architectures; organisations can safeguard their valuable assets and maintain business continuity amidst disasters.
DR Operations, specifically the concepts of switchover and failover, play a crucial role in disaster recovery planning. These terms may sound similar, but they have distinct meanings and purposes.
Switchover refers to the planned process of transitioning from one system or site to another without any disruption in service. It involves transferring operational responsibilities from the primary environment to a secondary one while maintaining continuous availability. Switchover is typically used for tasks such as routine maintenance or testing.
On the other hand, failover occurs when an unexpected incident causes an outage in the primary system. In this scenario, failover automatically redirects traffic and operations to a secondary or backup system that can take over seamlessly. Failover is designed to minimise downtime during unplanned events like hardware failures or natural disasters.
Both switchover and failover are essential components of a comprehensive disaster recovery strategy. They ensure continuity of operations by enabling organisations to quickly switch between systems or activate backups when needed most.
By implementing these DR operations effectively, businesses can mitigate potential disruptions caused by both planned activities and unforeseen events. Whether it's executing routine maintenance or responding to critical incidents, having robust switchover and failover processes in place ensures minimal impact on business operations and customer experience.
In addition to cost savings and increased accessibility, another benefit of leveraging the cloud for disaster recovery is improved security. Cloud service providers have robust security measures in place to protect against unauthorised access or data breaches. By entrusting their critical systems and sensitive information with reputable vendors who specialise in security protocols, organisations can gain peace of mind knowing that their data is protected even during unpredictable events.
When it comes to disaster recovery, having a DR site is crucial for ensuring business continuity. A DR site serves as a secondary location where operations can be shifted in the event of a disaster or outage at the primary site. The principles governing the design and implementation of DR sites are essential for maximising their effectiveness.
One important principle is geographic diversity. Ideally, a DR site should be located far enough away from the primary site to minimise the risk of both sites being affected by the same disaster or event. This ensures that even if one location experiences a disruption, operations can continue smoothly at the other.
Another key principle is redundancy. DR sites should have redundant infrastructure and resources in place to handle increased demand during failover scenarios. This includes duplicate servers, storage systems, network connectivity, and power sources to ensure uninterrupted service delivery.
Additionally, performance considerations play an important role in designing DR sites. The infrastructure at these locations should be capable of handling peak loads while maintaining acceptable response times for users accessing critical applications or services.
Security is also paramount when it comes to DR sites. Proper measures must be implemented to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance with industry regulations throughout all stages of disaster recovery operations.
Regular testing and maintenance are essential principles that cannot be overlooked. It's imperative to periodically test failover procedures and validate data integrity between primary and DR sites through rigorous testing protocols.
By following these principles when designing and implementing DR sites, organisations can greatly enhance their ability to recover quickly from disasters or outages without compromising on business continuity.
Disaster recovery is not just a buzzword or an optional consideration for businesses. It is a critical component of any organisation's overall IT strategy. The ability to recover quickly and efficiently from unexpected events can mean the difference between survival and failure.
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, downtime can have severe consequences, including financial loss, damage to reputation, and even legal implications. By investing in disaster recovery planning and implementation, companies can mitigate these risks and ensure business continuity.
It is essential to understand that disaster recovery goes beyond simply having backups or redundant systems in place. It requires careful planning, regular testing, and ongoing maintenance to stay effective. Regularly assessing potential threats and adjusting strategies accordingly is crucial for staying ahead of emerging risks.
Remember that no two organisations are exactly alike when it comes to their disaster recovery needs. Each company should tailor its approach based on its unique requirements, industry regulations, budget constraints, and risk tolerance levels.
While disaster recovery may seem like an overwhelming task at first glance, partnering with experienced professionals who specialise in this area can make all the difference. They bring expertise in designing comprehensive strategies tailored specifically to your business needs while staying within your budgetary constraints.
So, whether you're a small start-up or a multinational corporation, don't neglect the importance of disaster recovery planning. Take proactive steps today to protect your data assets and keep your operations running smoothly during times of crisis.
Remember: Disaster strikes without warning! Be prepared! And that wraps up our discussion on what disaster recovery is all about - how it helps businesses navigate through disruptions caused by natural disasters or technology failures! Stay safe!
Talk to us about your Disaster Recovery requirements.